담낭 = 쓸개 = GB = gallbladder
담낭 선근증= 담낭 선근종증 = 선근종성 증식증
Adenomyomatosis of GB = GB ADM = Adenomatous Hyperplasia of GB
복부 초음파 검사에서 우연히 발견되는 담낭 선근증에 대한 내용입니다.
대부분 무증상이며, 악성화 가능성은 드물다고 알려져 있습니다.
Gallbladder adenomyomatosis is a benign condition caused by exaggeration of the normal invaginations of the luminal epithelium (Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses) with associated smooth muscle proliferation. The affected areas demonstrate thickening of the gallbladder wall with internal cystic spaces, the key to the radiologic diagnosis. The great majority of adenomyomatoses are asymptomatic.
Adenomyomatosis may be focal or diffuse. The most common appearance on sonography is tiny, echogenic foci in the gallbladder wall that create comet-tail artifacts, presumably caused by either the cystic space itself or the internal debris. Prominent masslike focal areas of adenomyomatosis, called adenomyomas, are the next most common manifestation. Careful evaluation of the adenomyoma, sometimes requiring higher frequency or linear probes, can show several features that are diagnostic of the entity and allow for differentiation from neoplasm. The most diagnostic finding, although not the most common, is the presence of cystic spaces. Echogenic foci with comet-tail or “twinkling” artifact on Doppler examination are also typical. Focal adenomyomatosis is most common in the gallbladder fundus, less often narrowing the midportion of the organ, called hourglass gallbladder.
Fundal adenomyomas are often folded onto the body of the gallbladder and can occasionally be mistaken for a pericholecystic or even a hepatic mass. The entire gland wall may be involved, causing collapse of the lumen. The absence of the cystic spaces, echogenic foci, or twinkling artifact or the presence of internal vascularity should prompt further investigation to differentiate from neoplasm. MRI or MRCP allows for improved specificity, with the presence of cystic spaces within the thickened wall leading to the diagnosis.
Clinical Issues
• 9% prevalence in cholecystectomy specimens
• F > M; mean age: > 50 years
• Most often asymptomatic; or biliary pain/dyspepsia
• No conclusive evidence of increased cancer risk
• No clinical significance in asymptomatic patients when diagnosed correctly and differentiated from carcinoma

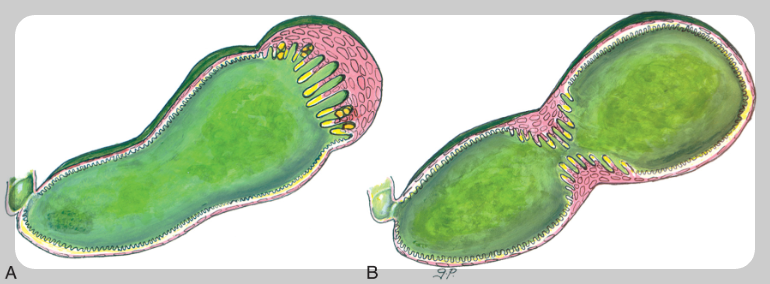
- Fundal type은 양성 질환.
- Segmental type은 반드시 주의 관찰 및 수술 고려.
- 증상이 있거나, 담석, 담낭염이 동반되는 경우 수술 고려.
- 담낭 선근증으로 인해 담낭암의 적절한 발견이 어려울 가능성이 있는 경우 수술 고려.
추적관찰은 영상학적으로 ADM 진단이 확실한 경우이므로,
애매한 경우에는 MR, EUS(내시경초음파) 검사를 위해 상급병원 전원이 필요합니다.
건진에서 우연히 담낭 선근증이 관찰되는 경우, 다음과 같은 결과표를 받게 됩니다.
내용대로 진행해주시면 됩니다.
* 복부 초음파 검사상 담낭 선근증 있습니다.
: 1년 뒤 추적관찰 받으십시오. 우상복부 통증이 발생한다면 진료 받으십시오.
* 복부 초음파 검사상 담낭 선근증 있습니다.
: 담석이 동반되어 있는 경우 담낭절제술을 고려합니다. 상의 위해 외과 진료 받으십시오.
* 복부 초음파 검사상 담낭 선근증 의심됩니다.
: 추가 검사(MR, EUS)를 고려하여 상급병원 소화기내과 진료를 권합니다.
(건진에서 추가 검사가 필요할 것으로 판단하여 의뢰하더라도,
실제 검사 진행은 상급병원에서 결정하게 됩니다.)
'건강검진 결과 > 영상 내시경 검사' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Phrygian cap GB (프리지안캡 담낭)_복부초음파 (0) | 2023.07.16 |
|---|---|
| 대장내시경에서 발견되는 이상소견 (게실, 흑색증) (0) | 2023.04.20 |
| 간역동 CT (역동적 조영증강 CT) (0) | 2022.03.21 |
| 헬리코박터균 (1) | 2020.05.19 |
| 대장 용종이란 (0) | 2020.05.11 |




댓글